Accurate invoicing processes in banks are essential to prevent revenue leakage and play a vital role in driving customer satisfaction. But despite best efforts, inaccuracies in invoices do happen. This is due to a variety of reasons ranging from data entry errors, incorrect pricing, to duplicate charges, and changes in product or service volumes. Addressing invoice anomalies efficiently is important to ensure financial accuracy, reduce costs, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure regulatory compliance. This article delves into the process of invoice anomaly detection, outlining its significance, and the steps involved in effectively managing invoice reviews and approvals.
Importance of Invoice Review
Invoice review and resolution are essential components of the invoicing and billing process. By meticulously reviewing and approving invoices, banks can prevent errors, comply with regulatory requirements, and uphold internal policies, which helps avoid legal and financial penalties. This process also ensures the accuracy of information provided to partners and customers, fostering trust and strengthening relationships. Overall, it contributes to a more transparent and reliable invoicing system, crucial for maintaining positive business relationships and operational integrity.
The Stages of Invoice Generation
Invoice generation comprises multiple stages. The first stage is that of a draft or pro-forma invoice which may or may not be subject to a review depending on predefined rules. If the rules call for a review, then it can either be approved or flagged for adjustments in the second stage. Once approved, it will move to the finalization stage. In case it is not approved, there will be further processes to make the necessary corrections. These may include repricing or set up adjustments. Once these changes are made and the invoice is approved, a final version is generated, which then moves to collection and payment.
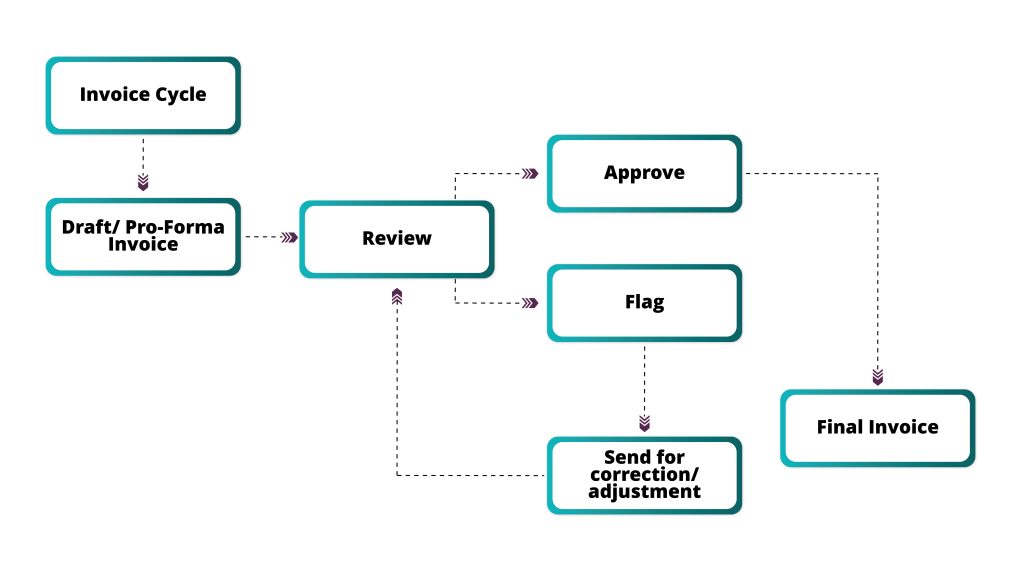
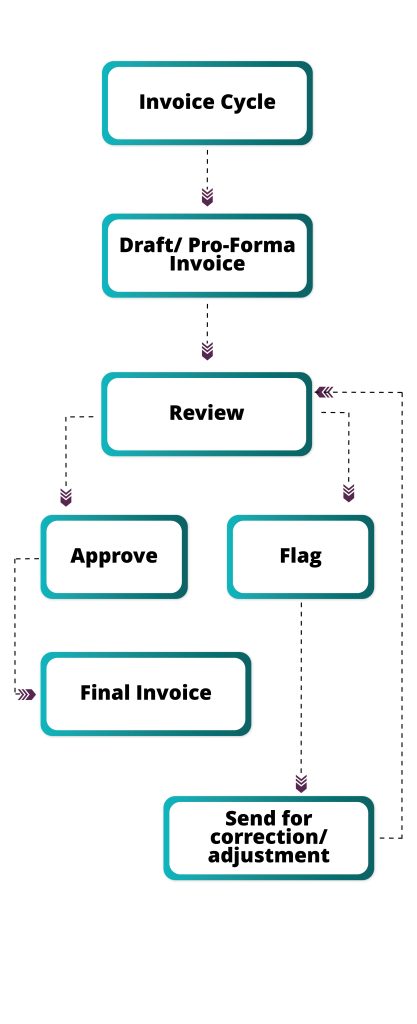
Review and Approval Process
There are some conditions for the review and approval of invoices. The bank may decide to review an initial pre-determined number of invoices for a customer or subscription. This is a good way to understand basic patterns and trends. It will ensure quick identification and mitigation of discrepancies in invoices. This is also invaluable for creating accurate trend patterns in a customer’s invoicing behavior. The bank may also decide to review invoices pertaining to a newly launched product or service. For customers who have been with the bank for a long time, anomaly detection can be more nuanced. This involves analyzing past data patterns and thresholds to identify any deviations.
Understanding Thresholds in Invoice Anomalies
Thresholds are acceptable limits for invoice amount variations. They are benchmarks against which new invoices are compared and are usually created after careful analysis of historical data that helps identify typical invoice amounts and fluctuation ranges. Different factors are taken into consideration when historical data is being categorized, such as organization/customer categories or even specific customer relationships.
A long-term customer may have well-established invoice variations and therefore have strict thresholds in place, while a new customer may need more flexible thresholds till a pattern is established. For example, when a new customer gets onboarded, the first ‘N’ months must be reviewed against the negotiated terms or applicable standard price agreements. This ensures that the invoices accurately reflect the contract with the customer.
Invoices must be grouped according to organization or customer categories or specific customers for error-free benchmarking. Historical data and threshold analysis is only the first step. Every customer must have acceptable deviation limits defined. This is done basis the analyzed data and considers factors like usage patterns, order sizes, and customer relationships. The bank must be able to take an informed decision on how much variation is permissible based on these limits. For example, if invoices vary by more than 10% from the average amount calculated from historical data, they are flagged for review. Alternatively, if an invoice amount exceeds a predefined threshold (e.g., USD1000), it is flagged. It is extremely important to update thresholds based on changing customer behavior, business trends, and evolving market dynamics, so that they remain accurate and help the organization correctly identify and rectify any discrepancies.
The next step is review and investigation. While specific methodologies vary from one bank to another, this is usually an automated process that calculates the difference in the new invoice from the historical average. Flagged invoices are then reviewed according to the established workflows. Workflows can be basic, where flagged invoices are made available for review and approval either through APIs, user interfaces, or other channels such as web portals, for the authorized staff members to review based on the SLA commitments with the customer. They can also be more complex and follow a multi-tier process, where the bank can define, review, and approve workflows based on the invoice amount or role of approvers. For example, a junior staff member is authorized to review invoices up to a certain value after which it is escalated to someone senior. Very high variances, or specific cases may require approvals from top management.
Analysis and Correction
Once an invoice has been flagged and reviewed it is crucial to understand why the variance occurred. A comprehensive root cause analysis that delves into underlying issues is crucial for preventing similar variances in the future. Root cause analysis involves verifying data, identifying errors in pricing and product definition, and determining missed adjustments like discounts, min/max schemes, free limits, etc. Corrective action must address the root cause with the objective of rectifying it. This may include steps like adjusting price points, ensuring necessary adjustments are carried out before the invoice cycle, and even reprocessing or repricing invoices if similar discrepancies keep occurring over a period. Comprehensive documentation through the entire process of invoice generation, review, and approval is vital for audit and compliance.
Leveraging Technology for Invoice Anomaly Detection
The question is, how can banks ensure that invoice anomalies are identified and addressed efficiently to minimize disputes and ensure efficient collections and payments? A robust, microservices-based, and cloud-native revenue management system is the answer. Such a platform can be configured to include applicable rule definitions and determine if invoices need review and approvals. Those that need approvals are automatically marked as “Pending” and once reviewed, the system can determine if the invoice is approved or rejected and take appropriate action. By automating the flagging process, such a platform can improve the efficiency of the invoice anomaly detection process and ensure timely rectification of key issues.
Effective invoice management is crucial in banks to minimize revenue leakage and ensure seamless revenue management. Identifying and addressing anomalies in invoices is an important part of the invoicing process, and a robust revenue management system can streamline it end to end to ensure accuracy and efficiency.








