The business of banking is facing some tough times. The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted markets and global economies at an unprecedented scale and the unexpected war in Ukraine only exacerbated the situation further. Today the banking sector must contend with a global slowdown on the one hand while also effectively meeting customer expectations and staving off competition from fintechs and tech giants. Banking profitability and revenue growth are of utmost importance now more than ever. Negotiations and deals have always been part of the corporate banking business, but now there must be a sharper focus on delivering personalized and relationship-based pricing for the customer, as well as profits for the bank in the long run. Deal management strategies that ensure effective analysis of business value, external influences, and cost influences are crucial for modern relationship managers looking to drive profitability.
Determine the Business Value of a Corporate Deal
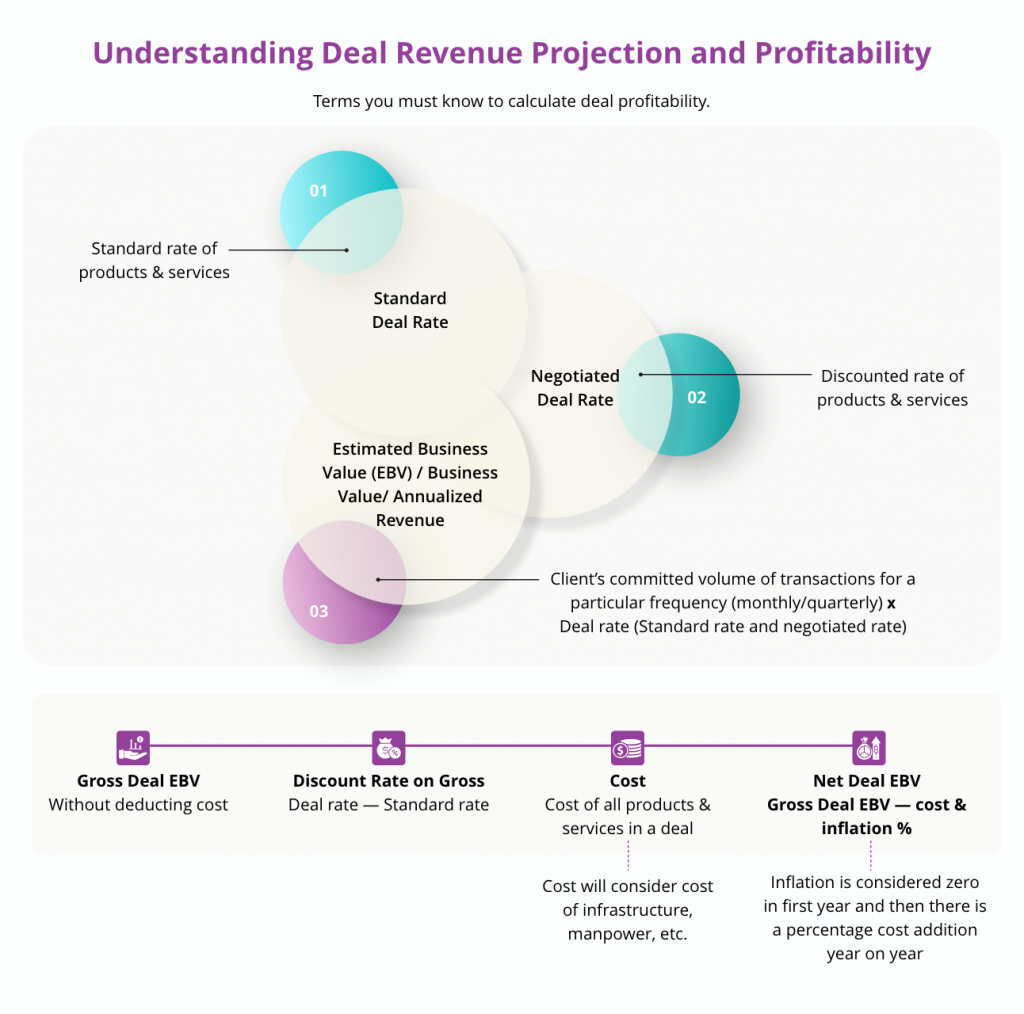
Deals are an integral part of corporate banking that are negotiated by the customer and the relationship manager. In corporate banking, a deal is usually applicable for more than a year. Within this period the deal may be impacted by several factors such as inflation, fluctuating interest rates, and other costs. For the financial institution to be profitable, the deal management process must focus not just on negotiability or discounts but also analyze its long-term financial soundness. Relationship managers must be able to identify a deal’s business value (BV) to understand if it will be profitable for the bank in the long run. Business value is a representative number based on specific parameters and inputs. It is the discounted deal rate being offered which is indicative of the estimated revenue the bank can expect from the deal. It forms the basis of every deal management profitability analysis in modern banking. The deal’s BV is determined by considering several factors. At the base level there are the deal details and customer commitments. This includes:
- Duration of the deal, currency, review frequency and number of reviews.
- Products, services, and offers included in the deal.
- Standard rates applicable.
- Negotiated rates being considered based on discussions with the customer.
- Customer commitments that could be volume based such as a minimum number of transactions during the specified time-period, or value based such as average ticket size against volume commitments during the specified period.
Using the above parameters, if a customer commits to 100 transactions a year, the BV can be arrived at by taking into consideration the commitments provided by the customer, the negotiated rates offered by the bank and forecasting the revenue from the deal basis the parameters.
Profitability Analysis with a Focus on Cost
But a deal’s profitability is not just determined by customer’s commitment and negotiated price alone. There are also additional factors that must be considered when calculating the BV such as costs, inflation and discount ratio. The final expected revenue can only be calculated by factoring these into the calculations. Inflation, or the value of currency is a serious challenge that impacts business and deal life itself.
Inflation Ratio and Discount Ratio
Currently the world is witnessing soaring inflation rates leading to central banks hiking interest rates. The impact on banking is significant with a slowdown in borrowing. Naturally, inflation rates must also be considered when calculating the BV and expected profitability of a deal. This is because the cost or the value of the currency when the deal is being made may not remain the same a year later. If a long-term contract is drawn up without considering the impact of inflation, it may not remain profitable as time passes. A cutting-edge deal management and revenue management system must provide revenue managers with a reference library that they can use to input the inflation values in the BV calculation. Direct input based on real world conditions can also be enabled in an advanced deal management system if allowed by the institution. A discount rate is the rate of return that is applied on the present system and is another important parameter that is used to measure the Net Present Value (NPV). This too is usually available in a reference library and must be incorporated when calculating BV and estimated revenue.
Other Cost Influences on Profitability
In addition to inflation and discount rates, there are some other cost influences that must be factored into the BV and expected revenue calculation. Cost influence may include factors such as expenditure pertaining to provision, maintenance, and distribution of products and services, hardware and software costs, partner and vendor costs, personnel costs, and marketing costs. Costs can be defined at product or service level, and there can be multiple costs at any level. Costs can also be associated with offers.
Costs can be categorized into two, and total cost to be considered for calculating BV includes both the categories.
- Cost built into the product, service, or offer.
- Direct cost, which is the cost that is added as part of the deal. In other words, it is the expenditure incurred while creating, maintaining, or tracking a deal. This can be at different levels such as at the overall deal level, or applicable to each product and service under the deal. It may be applicable to standalone services subscribed, or at charges level across entities or even on individual offers.
Each of the factors detailed above have a significant bearing on profitability. The cost to income ratio determines what percentage of the total revenue are connected to the costs. The Projected Deal Profitability is the net present value of the profit or Net Deal Revenue over the net present value of the gross revenue.
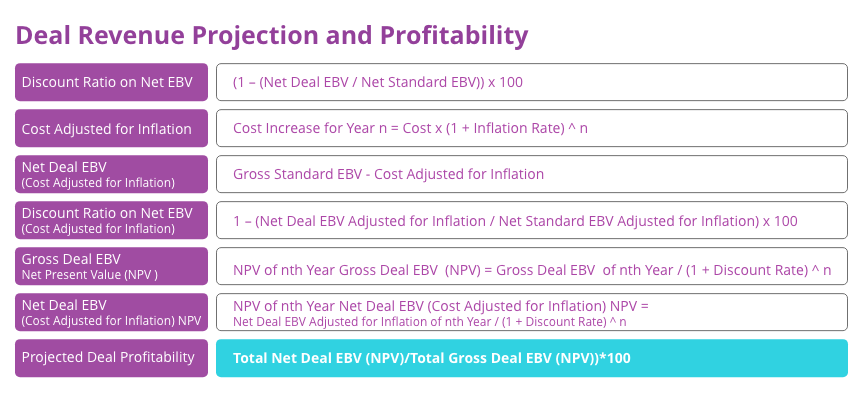
Revenue projection and profitability analysis is a critical part of the deal management process. The EBV or business value is just the basis for this. It needs to be bolstered further by considering other inputs. Some of the factors to be considered include cost to income ratio, discount rate, and inflation percentage. Inflation is an external factor that plays a crucial role in revenue projections. It takes into account that the value of currency may fluctuate over time. For multi-year contracts particularly, this is extremely important as the cost considered while making the deal may not remain the same while the deal is being implemented. Costs must be adjusted for inflation when calculating revenue projections.
SunTec Deal Management
SunTec Deal Management helps to automate the process of creating, calculating, managing, and measuring deals. Its data-driven process ensures greater transparency, more accurate sales forecasting, and deal profitability analysis. The platform’s intelligent deal pricing capabilities can help relationship managers simulate expected revenue and conduct profitability analyses based on throughputs and price points. This is a significant advantage to them as they carry out price negotiations. The platform can help enhance the sales process, simplify complex negotiations, and streamline billing operations as well. The contextual solutions and right pricing offered can help drive a better customer experience. In addition to driving relationship value with personalized offerings, the platform provides the right insights for each stage of the sales process. With SunTec Deal Management relationship managers can effectively calculate deal profitability and BV of every deal to ensure the financial institution remains profitable and continues to grow its revenues.








